The Future of Language Learning: Embracing Innovation in a Globalized World
AI and Language Learning: Can Technology Replace Teachers?
For years, there has been growing speculation that artificial intelligence (AI) is advancing rapidly and that it may one day surpass human capabilities or even replace humans in numerous fields. With its unparalleled ability to process vast amounts of data and continuously learn, AI is often perceived as an exceptional source of knowledge. This raises a profound question in education: Can AI truly replace teachers and revolutionize traditional learning methods?
Because of a significant technological change happening right before us, the future of language learning offers a fascinating case study. With AI-driven tools becoming increasingly advanced, from interactive platforms to personalized tutors, we are witnessing a transformation in how languages are taught and learned. However, can these innovations fully replace human educators?
In the conversation for Stanford Engineering Staff, a cognitive scientist and an expert in language learning, Michael Frank, highlights a significant "data gap" between the vast amount of language data AI like ChatGPT is exposed to (500 billion words) and the limited exposure of toddlers (15 million words), emphasizing at the same time that children's learning occurs in rich social contexts, unlike AI.
Children learn language in a multimodal, social environment with sensory experiences (sight, touch, sound), allowing them to infer unstated meanings and understand cultural cues. Pointing this out, Michael Frank proves that this richness in context contrasts with AI's data-driven language acquisition. While AI can produce grammatically correct sentences, children learn from real-life interactions. AI lacks the social, sensory, and contextual aspects of human learning.1
Given the vast differences between how babies acquire language and how AI processes it, we can conclude that the human element is irreplaceable. Human interaction is essential for learning and growth. However, technology can still play a vital role in enhancing this process. As Steve Jobs, co-founder of Apple, wisely stated:
"Technology is nothing. What's important is that you have faith in people, that they're good and smart, and if you give them tools, they'll do wonderful things with them."
In fact, in an era when globalization's effects are widely visible, the rise of technology in language learning is not only gaining momentum but also reshaping the educational landscape. As digital tools become more sophisticated, their importance in mastering new languages is undeniable, offering unprecedented opportunities for learners to immerse themselves in diverse linguistic environments. With the potential to revolutionize traditional methods, technology holds the power to make language acquisition more efficient, accessible, and transformative than ever before, positioning itself as a cornerstone of future education.
This article explores the evolving landscape of language learning using technology tools, examining the developing market and its offerings. It will analyze present trends and modern directions.

Improve, discover, build, and return home with recognised certificates.
The Evolution of Language Learning Market
The language learning market has experienced substantial growth over the past decade and is projected to expand even more rapidly in the coming years.
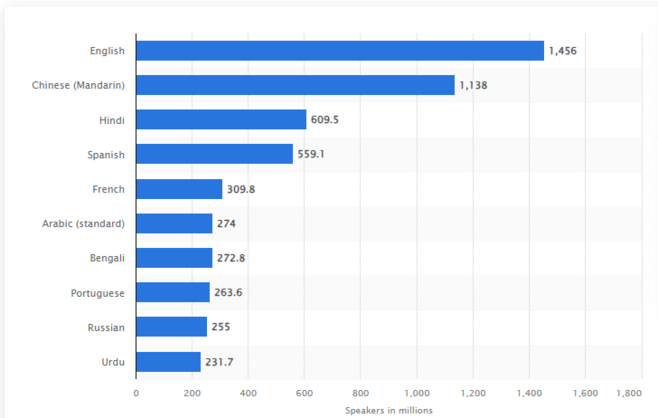
The most spoken languages worldwide in 2023 (by speakers in millions)
English plays a vital role in this growth, being the most widely spoken language globally. According to research from Statista, approximately 1.5 billion people worldwide spoke English as their native or second language in 2023, slightly surpassing the 1.1 billion speakers of Mandarin Chinese. Hindi and Spanish were the third and fourth most spoken languages that year.2
Given English's status as the most popular language to learn, it's unsurprising that the English-as-a-foreign-language (EFL) sector represents a significant portion of the overall market.
As we can see in the graphic above, in 2023, Europe accounted for over 30% of the global language-learning market.
This dominance is fueled by the rapid implementation of 5G technology, supported by the region's robust digital infrastructure and widespread internet access, making language education highly accessible across the continent.
Additionally, Europe's multilingual environment plays a significant role, as different languages frequently surround people and often move between countries.
Unlike in regions such as the Americas, where entire continents primarily share a common language, Europe's linguistic diversity further drives the demand for language learning.
According to GSMA, 5G adoption in Europe reached over 11% in 2022 and is projected to surge to 87% by 2030. The capabilities of 5G, such as delivering high-definition videos and incorporating Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) elements, can significantly enhance language learning.
With 5G's high speed and low latency, learners can engage in immersive language simulations, virtual practice sessions, and 360-degree cultural experiences, making the process more interactive and engaging.
Consequently, mobile learning apps, cloud-based platforms, and online collaboration tools are driving the growth of the language learning market in Europe.

With SPRACHCAFFE, you take the direct route to your designated university.
AI-Powered Language Apps and Platforms
The market offers a wide range of apps and platforms to learn languages. We observe the increasing incorporation of AI and natural language processing (NLP) technologies into language learning. These innovations facilitate:
- advanced speech recognition,
- immediate feedback on pronunciation and grammar,
- intelligent tutoring systems,
- virtual language assistants,
- and chatbot assistance for language practice and conversation.
It creates interactive opportunities for practice and conversation. It allows learners to participate in dialogues, pose questions, and receive immediate responses, enhancing their language skills and building conversational confidence.
By leveraging AI and NLP, language learning platforms can offer personalized experiences tailored to individual learners.
They analyze various learner data, including proficiency levels, learning styles, and preferences, to provide customized content, adaptive assessments, and personalized learning pathways.
This level of personalization not only improves the effectiveness of their learning but also makes learners feel more catered to and valued, enhancing their engagement.
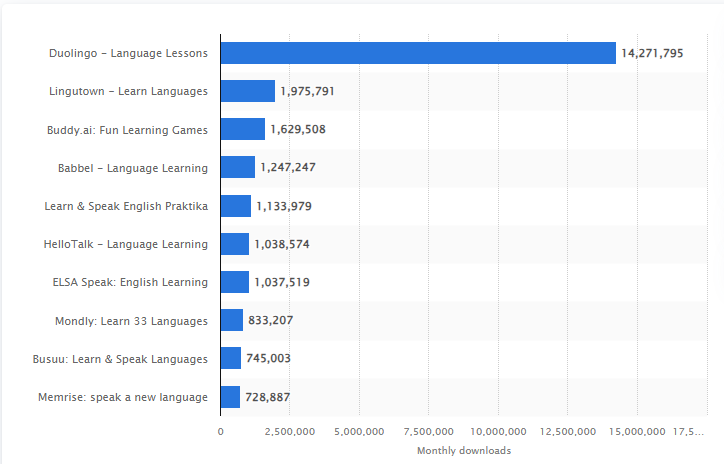
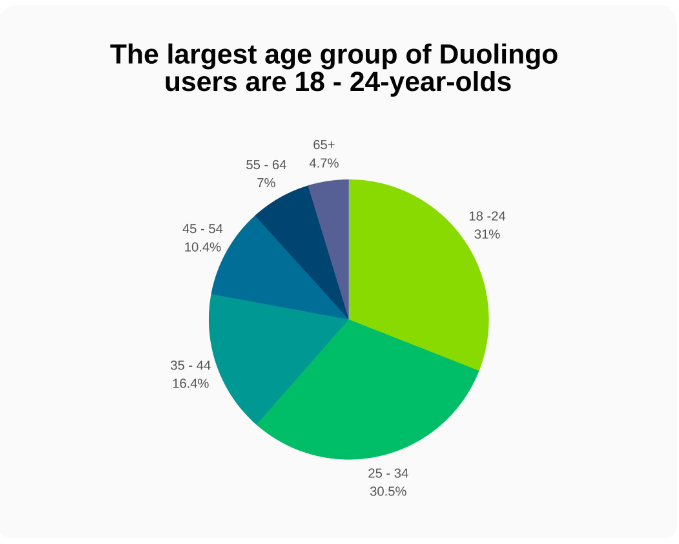
Duolingo - the most popular language learning app
In 2024, Duolingo is still the leading language learning app globally, achieving approximately 14.3 million downloads for mobile devices. This surge in downloads underscores the app's popularity and the growing interest in digital language learning solutions .5
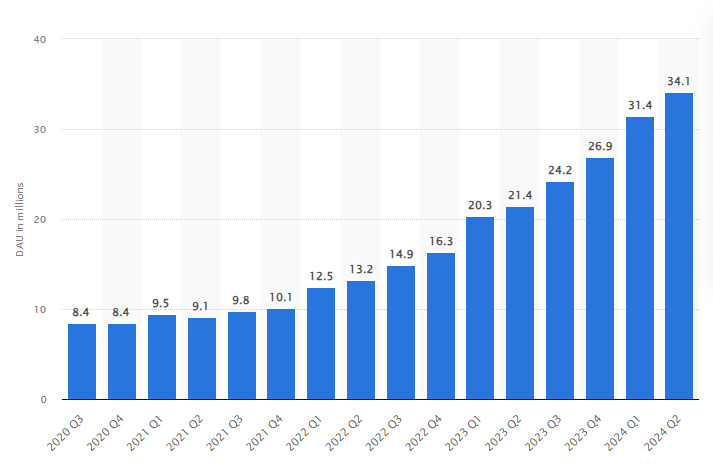
The focus extends beyond download numbers and includes daily active users (DAU). In Q1 of 2024, Duolingo reported around 34 million DAUs engaging with their chosen languages on the platform.
This marks a nearly 60% increase compared to the previous year and a quarterly growth of about 9%. Duolingo's DAU has consistently risen from the Q3 of 2020 through early 2024.6
Duolingo and Technology
- Duolingo's machine learning algorithms accurately track user progress and learning patterns. This data is then used to tailor lessons, adjust difficulty levels, revisit weak areas, and introduce new content at the most opportune moments. This adaptability ensures that each user's learning journey is personalized and optimized.
- Its AI engine, "Birdbrain," evaluates which exercises are best suited for each learner based on their prior responses. It continuously fine-tunes lesson content to challenge users just enough without overwhelming them. By analyzing when learners are most likely to forget the material, Birdbrain schedules review sessions using a spaced repetition technique. This method ensures users retain knowledge over time by revisiting material before they are likely to forget it.
- Duolingo employs speech recognition technology for speaking exercises. This allows users to practice pronunciation and receive real-time feedback on how accurately they are pronouncing words and phrases.
- To keep users engaged, it adjusts game-like features such as difficulty levels, streak challenges, and rewards, ensuring that learning feels achievable but challenging.
- Recently, Duolingo has also introduced a new video game-like experience, Adventures, where you become one of the Duolingo characters and have a task to complete, like ordering coffee, grocery shopping, or asking for directions. These experiences help the learners put into practice everything they have learned.
- Duolingo's machine learning algorithms accurately track user progress and learning patterns. This data is then used to tailor lessons, adjust difficulty levels, revisit weak areas, and introduce new content at the most opportune moments. This adaptability ensures that each user's learning journey is personalized and optimized.
- Its AI engine, "Birdbrain," evaluates which exercises are best suited for each learner based on their prior responses. It continuously fine-tunes lesson content to challenge users just enough without overwhelming them. By analyzing when learners are most likely to forget the material, Birdbrain schedules review sessions using a spaced repetition technique. This method ensures users retain knowledge over time by revisiting material before they are likely to forget it.
- Duolingo employs speech recognition technology for speaking exercises. This allows users to practice pronunciation and receive real-time feedback on how accurately they are pronouncing words and phrases.
- To keep users engaged, it adjusts game-like features such as difficulty levels, streak challenges, and rewards, ensuring that learning feels achievable but challenging.
- Recently, Duolingo has also introduced a new video game-like experience, Adventures, where you become one of the Duolingo characters and have a task to complete, like ordering coffee, grocery shopping, or asking for directions. These experiences help the learners put into practice everything they have learned.
Are language learning apps effective?
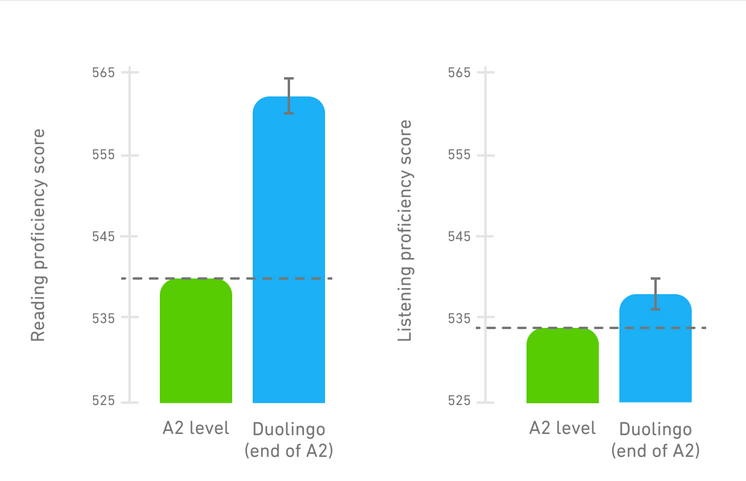
Duolingo experts research to study the effectiveness of the methods used in the app. The technology used in Duolingo courses has proven to improve all learners' language skills. For instance, one study, where Spanish, Portuguese, and Japanese learners completed the A2 CEFR (Common European Framework of Reference for Languages) level of English course on Duolingo, showed that the learners scored above the expected level. Another study shows that after completing five sections on Duolingo, learners of French and Spanish reached a proficiency level comparable to university students who had taken five semesters of language courses. This point in the course represents approximately half of the content needed to reach the B1 level.9
Preply and AI
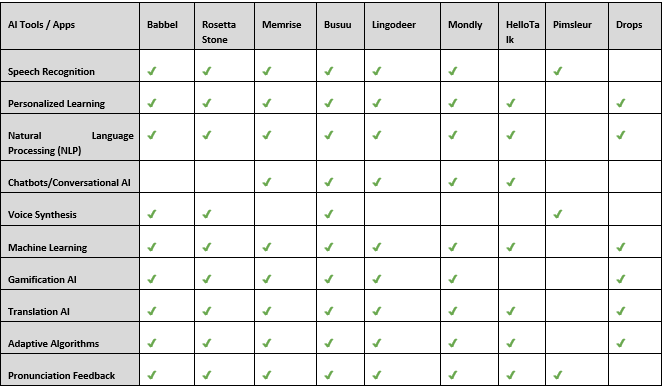
Apart from Duolingo, there are a number of apps and platforms that utilize AI-powered tools. The table highlights that most language apps utilize available AI tools, such as personalized learning and machine learning, to enhance user experience and optimize learning outcomes. These technologies are integral to modern language acquisition, enabling more effective and tailored educational approaches.
Preply, a language learning platform connecting students with over 35,000 tutors across 50 languages, raised an additional $70 million in 2023, as TechCrunch reports, extending its Series C funding to $120 million.
Horizon Capital led the round, with participation from edtech-focused Reach Capital, Owl Ventures, and others.
Of the $70 million, 60% ($42 million) is equity, and $28 million is debt.
Preply, originally founded in Ukraine, plans to use this funding to enhance its AI capabilities. While human tutors remain central, AI will help scale learning, improve access, and assist with tasks like creating exercises, grammar explanations, and tracking student progress.
The company's growth has been strong, especially amid the challenges of the ongoing war in Ukraine, with its sales growing tenfold in the last three years.
VR and AR - futuristic gadgets or cyber revolution?
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies offer powerful tools to enhance language learning by creating highly immersive, interactive, and contextualized learning experiences.
These technologies significantly differ from traditional learning methods in how they cognitively and emotionally engage learners.
Immersive Learning Environments
The essential advantage of VR in language learning is its ability to simulate real-world environments. Learners can practice conversations virtually without the social pressure of making mistakes.
This practical application of language skills leads to more effective learning and memory retention.
According to a Stanford University study, students using VR to participate in virtual language lessons showed increased engagement and retention due to heightened spatial presence and interactivity .
This sense of immersion allows learners to feel like they are indeed "in" the environment, which enhances their ability to recall vocabulary and phrases through contextual memory.10
The Role of AR in Contextual Learning
AR, conversely, integrates virtual information with the real world, enabling learners to translate and understand language in context.
The article "Enhancing Learning and Productivity with Google Lens" explores how Google Lens assists students and educators by leveraging machine learning through smartphone cameras. Available for Android and iOS, Google Lens has evolved since its launch in 2017, now offering a variety of features such as image identification, real-time text translation, and text-to-audio conversion. Especially beneficial for ESL students. 11
In an episode of the "Teachers Talk Tech" podcast, Dr. Mark Pegrum and Andrea Vinkler discuss the educational potential of augmented reality in language learning. They highlight that AR enriches real-world environments by overlaying digital content, while VR creates fully immersive digital worlds. 12
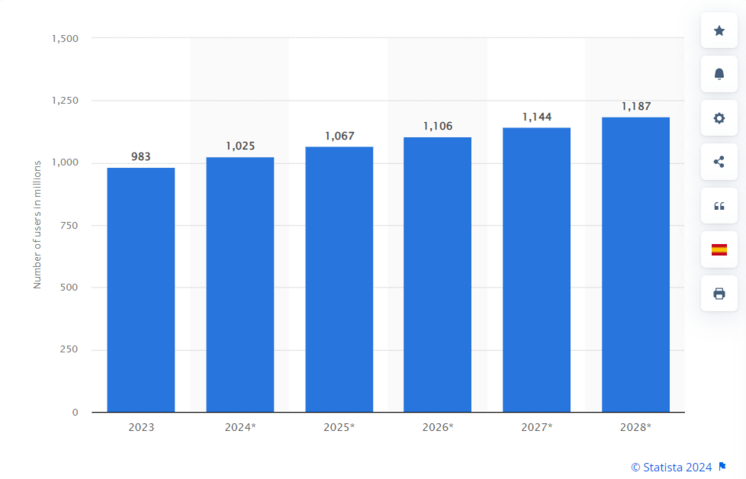
According to recent data provided by Statista, there are about 1 billion mobile augmented reality (AR) user devices worldwide now, and the number is expected to grow steadily to reach about 1.2 billion AR users in 2028. This shows promise in the availability of the newest technology to new potential students.
Psychological Benefits
VR and AR enhance traditional learning by offering more engaging ways to interact with the material.
According to research from Syracuse University, students using immersive VR-based learning environments outperformed those using desktop-based or traditional methods by 30% in memory retention tests. Spatial presence in VR has been shown to correlate with enjoyment and motivation, influencing how students engage with educational content. Enjoyment is also closely linked to intrinsic motivation, suggesting that activities perceived as enjoyable can further increase learners' motivation to participate in educational tasks. This improvement in memory retention is attributed to the multi-sensory nature of VR, which effectively taps into how humans naturally learn through physical experience and emotional engagement.13
Source: https://surface.syr.edu/thesis/204/
Enhanced Engagement and Retention
Immersive environments also benefit from what is known as the "embodied cognition" effect, where learners can associate new language skills with physical actions or locations in the virtual space.
A study from MIT on language learning through VR by Christian David Vázquez Machado discusses how the physicality of language - connecting words to bodily movements - can enhance language learning. Research shows that using gestures and actions when learning new words improves recall and retention. Vázquez Machado mentions a VR platform called Words in Motion, developed by the MIT Media Lab, which integrates kinesthetic interactions into virtual environments.
For example, users can learn the Spanish word "pintar" by performing painting actions with a virtual brush and the word would appear in the virtual space. This approach allows learners to interact with words contextually. The study conducted with 60 university students learning new Spanish words demonstrated the promising potential of kinesthetic learning in VR. It significantly improved long-term retention compared to traditional text-based methods. Although text-based learners initially outperformed those in VR, the kinesthetic VR group retained more vocabulary over time, hinting at the bright future of VR in language learning.14
Apps utilizing new technologies
Language learning apps that utilize virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) create immersive environments. These environments allow users to practice real-world conversations and enhance vocabulary retention through interactive and engaging simulations.
Mondly VR, an extension of the Mondly language learning app, offers a virtual reality language learning Eexperience through Extensive Learning, Immersive Vocabulary, and Immersive Conversations. The most VR-native is the Immersive Conversations Mode, where users interact with animated characters in realistic scenarios like train rides and taxi conversations, offering more dynamic and memorable learning opportunities. Although still in development, Mondly VR shows potential for creating genuinely immersive, VR-native language learning experiences.14
ImmerseMe, on the other hand, emphasizes total immersion in various cultural and everyday scenarios. The platform offers nine languages and allows users to participate in role-playing activities like shopping at a market or interacting at a business meeting, helping them build confidence in speaking and comprehension. ImmerseMe's VR simulations also focus on pronunciation and fluency, providing instant feedback on errors and guiding learners to improvement.
In conclusion, VR and AR offer learners an innovative way to practice language skills and enhance cognitive and emotional engagement, improving long-term retention and making language learning more accessible in real-world settings. These technologies represent a future where language barriers may become increasingly insignificant.
Translation tools in language learning
As AR glasses and real-time translation technologies continue to advance, the future of language learning will likely include fully immersive AR experiences where learners can translate conversations in real-time or receive language cues in their natural surroundings.
Translation technology, such as Google Translate or DeepL, is rapidly transforming language learning by offering real-time speech and text translations. These tools are versatile, empowering users to navigate a variety of language-related situations. For example, travelers can use these devices to translate menus, street signs, or conversations, immersing themselves in real-world language use. In a business context, these tools remove communication barriers, enabling professionals to negotiate and collaborate globally without the need for fluency in multiple languages.
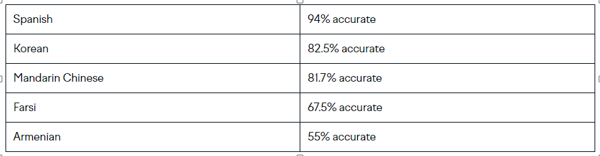
Source: https://lokalise.com/blog/google-translate-accuracy/
DeepL primarily distinguishes itself from Google Translate by emphasizing producing more natural and contextually accurate translations, especially in European languages. While Google Translate uses Neural Machine Translation (NMT), DeepL focuses on capturing linguistic nuances and delivering more human-like translations. DeepL's neural networks are often trained with a more targeted dataset, allowing for improved fluency and tone in complex translations. Additionally, users often report that DeepL excels in handling idiomatic expressions and technical texts, making it a popular choice for professional translations. While Google Translate covers a broader range of languages, DeepL's narrower focus enables it to offer more refined translations for its supported languages.17 The evolution of language translation is also palpable through AI. The Large Language Models (LLMs), like ChatGPT, are models that can serve as a translation tool thanks to their training on vast datasets for a variety of languages. While they can effectively translate complex sentences and navigate subtle shifts in meaning, their translations are based on statistical patterns rather than genuine comprehension. AI has made significant strides in translation. However, human oversight remains essential, particularly for tasks requiring deep cultural understanding and nuance.18
Translation gadgets
Naturally, the market for translation gadgets is also blooming. At CES 2024 (Consumer Electronics Show), Timekettle X1 Interpreter Hub was launched-a groundbreaking translation device that can support multi-language translation for up to 20 people simultaneously, both online and offline. It allows participants to communicate in different languages in real time, with features like Face-to-Face Conversation Mode and Speak Mode for handheld use. The device is intended for business and educational use, offering innovative options like meeting recording and upcoming AI-driven voice cloning for translations.19
Similarly, Vasco Electronics introduced a real-time translation earpiece at the same event in 2024. Vasco's device enables conversations where participants speak different languages yet understand each other through live translation. The CEO of Vasco Electronics, Maciej Góralski, envisions a future where language learning declines as real-time translation tools make it easier to communicate across languages.20
Both the Timekettle X1 and Vasco Electronics earpiece offer practical tools that can significantly enhance language learning in real-world environments. By providing real-time translation during conversations, these devices allow their users to engage with native speakers and understand context and nuances in a natural setting, reinforcing their language skills.
In the future, such real-time translation devices will support immediate communication and serve as learning aids. As these tools improve through machine learning, they will provide more precise and context-sensitive translations, allowing language learners to receive instant feedback on vocabulary and grammar.
Do we need to learn languages or is technology the answer to everything?
In today's world, the proliferation of technology and translation tools may suggest that learning languages are becoming essential. While tools like Google Translate facilitate instant communication across linguistic barriers, they cannot fully capture human language's nuances, cultural contexts, and emotional subtleties. Learning a language fosters deeper connections, enhances cognitive skills, and enriches cultural understanding. Moreover, proficiency in a language can be a significant advantage in professional settings, where nuanced communication is crucial. Thus, while technology provides convenience, learning languages remains vital for personal and professional growth
The Limitations of Technology in Language Learning
The potential of technology in language learning is vast, with AI-powered tools, VR, and AR creating immersive, interactive experiences that enhance engagement, retention, and personalization. AI-driven apps like Duolingo offer adaptive learning paths, speech recognition, and real-time feedback, while VR and AR bring real-world simulations into language practice. These innovations make language acquisition more accessible, efficient, and enjoyable, revolutionizing how learners approach new languages.
However, the limitations of technology in language learning must also be acknowledged.
- First, AI lacks the social, cultural, and emotional nuances that human interaction provides, which are critical for understanding context and meaning in language use. This significantly limits the immersive experience. While AI tools like Google's Bard are improving, natural, fluent conversation with AI is not yet fully developed.
- Secondly, over-reliance on technology can lead to shallow learning, with users focusing more on gamified elements than deep linguistic comprehension.
- Next, technological disparities can create a learning divide, with underprivileged students lacking access to advanced AI tools. This gap may widen, leaving some learners behind as AI-based education grows.
- What is more, overreliance on AI may stunt critical thinking and creativity. There's also concern about students submitting AI-generated work, pushing educators to use tools like Turnitin, which now detects AI-generated content. It's a constant race between evolving AI and plagiarism detection systems.
- Finally, technology can only sometimes adapt to learners' unique emotional and psychological needs, something teachers excel at.
Traditional language learning and technology can work together by combining human-led instruction with digital tools. Teachers can use technology to supplement lessons, provide personalized practice, and engage students while fostering the social, emotional, and cultural aspects of language learning that only humans can provide. This hybrid approach offers the best of both worlds.
Traditional language learning and technology can work together by combining human-led instruction with digital tools. Teachers can use technology to supplement lessons, provide personalized practice, and engage students while fostering the social, emotional, and cultural aspects of language learning that only humans can provide. This hybrid approach offers the best of both worlds.
To sum up, the future of language learning is an exciting blend of technology and human experience, offering deeper engagement and accessibility. While AI and immersive tools like VR and AR reshape the landscape, human educators remain essential in guiding learners through social and emotional dimensions.
"It is the supreme art of the teacher to awaken joy in creative expression and knowledge." - Albert Einstein
Traditional language learning and technology can work together by combining human-led instruction with digital tools. Teachers can use technology to supplement lessons, provide personalized practice, and engage students while fostering the social, emotional, and cultural aspects of language learning that only humans can provide. This hybrid approach offers the best of both worlds.
To sum up, the future of language learning is an exciting blend of technology and human experience, offering deeper engagement and accessibility. While AI and immersive tools like VR and AR reshape the landscape, human educators remain essential in guiding learners through social and emotional dimensions.
"It is the supreme art of the teacher to awaken joy in creative expression and knowledge."
Albert Einstein
Additional fun reads on the subject:
- AI enabled sign language recognition and VR space bidirectional communication using triboelectric smart glove
- The Motive VR Training Platform for Empathy Training in VR
References:
1 Stanford Engineering Staff. (2024, February 9). The future of language learning. Stanford University. https://engineering.stanford.edu/news/future-language-learning
2 Dyvik, E. H. (2024, July 4). The most spoken languages worldwide. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/266808/the-most-spoken-languages-worldwide/
3 Tech Report. (2024, June 4). Language learning market statistics. Tech Report. https://techreport.com/statistics/language-learning-market-statistics/
4 Global Market Insights. (2024, June). Language Learning Market Size - By Language (English, Spanish, German, Chinese, French, Russian, Portuguese, Italian), Learning Mode (Offline, Online), End User (Individual Learner, Academic Learner, Corporate Learner), Learning Type & Forecast, 2024 - 2032. Global Market Insights. https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/language-learning-market
5 Ceci, L. (2024, August 29). Leading language learning apps worldwide in July 2024, by downloads. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1239522/top-language-learning-apps-downloads/
6 Ceci, L. (2024, August 29). Number of daily active Duolingo users worldwide from 3rd quarter 2020 to 2nd quarter 2024. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1309604/duolingo-quarterly-dau/
7 Sign House. (2024). Duolingo users and growth statistics (2024). Sign House. https://usesignhouse.com/blog/duolingo-stats/#who-is-duolingo%E2%80%99s-target-audience
8 Sign House. (2024). Duolingo users and growth statistics (2024). Sign House. https://usesignhouse.com/blog/duolingo-stats/#duolingo-users-by-age
9 Jiang, X., Peters, R., Plonsky, L., & Pajak, B. (2024, March 25). The effectiveness of Duolingo English courses in developing reading and listening proficiency. CALICO Journal. https://journal.equinoxpub.com/Calico/article/view/26704
10 Stanford Report. (2022, December 14). New Stanford study shows choices of virtual environments and avatars can promote positive psychological outcomes in the metaverse. Stanford University. https://news.stanford.edu/stories/2022/12/vr-real-impact-study-finds
11 Tip of the Month - Teaching and Learning Toolbox. (2021, November 30). Enhancing learning and productivity with Google Lens! Teaching and Learning Toolbox. https://teachingandlearningtoolbox.wordpress.com/2021/11/30/enhancing-learning-and-productivity-with-google-lens/
12 Cambridge - Teachers Talk Tech. (2022, May 31). Using augmented and virtual reality in language teaching. Cambridge University Press. https://www.cambridge.org/elt/blog/2022/05/31/augmented-virtual-reality-language-teaching/
13 Syracuse University Library. (2018, May). How spatial presence in VR affects memory retention and motivation in second language learning: A comparison of desktop and immersive VR-based learning. Syracuse University. https://surface.syr.edu/thesis/204/
14 MIT Media Lab. (2018, June 19). Kinesthetic language learning in virtual reality. MIT Media Lab.
Author: Sylwia Stryjewska, Teacher, methodologist and teacher trainer, coordinator of educational projects